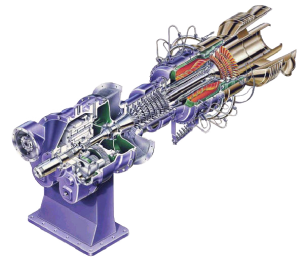
 A gas turbine engine is a type of internal combustion engine. Essentially, the engine can be viewed as an energy conversion device that converts energy stored in the fuel to useful mechanical energy in the form of rotational power. The term “gas” refers to the ambient air that is taken into the engine and used as the working medium in the energy conversion process.
A gas turbine engine is a type of internal combustion engine. Essentially, the engine can be viewed as an energy conversion device that converts energy stored in the fuel to useful mechanical energy in the form of rotational power. The term “gas” refers to the ambient air that is taken into the engine and used as the working medium in the energy conversion process.
This air is first drawn into the engine where it is compressed, mixed with fuel and ignited. The resulting hot gas expands at high velocity through a series of airfoil-shaped blades transferring energy created from combustion to turn an output shaft.
The residual thermal energy in the hot exhaust gas can be harnessed for a variety of industrial processes.



Submersible Pumps

A submersible pump is a device which has a hermetically sealed motor close-coupled to the pump body. The whole assembly is submerged in the fluid to be pumped.
The main advantage of this type of pump is that it prevents pump cavitation, a problem associated with a high elevation difference between pump and the fluid surface.
Submersible pumps push fluid to the surface as opposed to jet pumps having to pull fluids. Submersibles are more efficient than jet pumps.